
V tomto tutoriálu vám ukážeme, jak nainstalovat a nakonfigurovat Ntopng na Ubuntu 16.04. Pro ty z vás, kteří to nevěděli, je Ntopng poměrně užitečným nástrojem, pokud chcete monitorovat různé síťové protokoly na vašich serverech. Poskytuje spoustu nástrojů pro monitorování různých protokolů, variant provozu a ano, šířky pásma v různých časových rámcích. Ntopng je založen na libpcap a byl napsán přenosným způsobem, aby mohl virtuálně běžet na každá platforma Unix, MacOSX a také na Win32.
Tento článek předpokládá, že máte alespoň základní znalosti Linuxu, víte, jak používat shell, a co je nejdůležitější, hostujete svůj web na vlastním VPS. Instalace je poměrně jednoduchá a předpokládá, že běží v účtu root, pokud ne, možná budete muset přidat 'sudo ‘ k příkazům pro získání oprávnění root. Ukážu vám krok za krokem instalaci Ntopng na server Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus).
Nainstalujte Ntopng na Ubuntu 16.04
Krok 1. Nejprve zkontrolujte, zda je universální úložiště povoleno, a to kontrolou ‘/etc/apt/sources.list ‘ s vaším oblíbeným editorem.
sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list
Pokud vesmír není zahrnut, upravte soubor tak, aby ano:
deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial main universe
Krok 2. Instalace Ntopng.
Chcete-li nainstalovat Ntopng, spusťte následující příkaz jako uživatel root:
sudo apt-get install redis-server sudo apt-get install ntopng
Krok 3. Nakonfigurujte Ntopng.
Vytvořte konfigurační soubor Ntopng. V tomto článku používáme nano jako textový editor. K vytvoření konfiguračních souborů Ntopng můžete použít svůj oblíbený textový editor:
sudo nano /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf
# /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf # # The configuration file is similar to the command line, with the exception that an equal # sign '=' must be used between key and value. Example: -i=p1p2 or --interface=p1p2 For # options with no value (e.g. -v) the equal is also necessary. Example: "-v=" must be used. # # # -G|--pid-path # Specifies the path where the PID (process ID) is saved. # -G=/var/tmp/ntopng.pid # # -e|--daemon # This parameter causes ntop to become a daemon, i.e. a task which runs in the background # without connection to a specific terminal. To use ntop other than as a casual monitoring # tool, you probably will want to use this option. # -e= # # -i|--interface # Specifies the network interface or collector endpoint to be used by ntopng for network # monitoring. On Unix you can specify both the interface name (e.g. lo) or the numeric # interface id as shown by ntopng -h. On Windows you must use the interface number instead. # Note that you can specify -i multiple times in order to instruct ntopng to create multi‐ # ple interfaces. # -i=1 # # -w|--http-port # Sets the HTTP port of the embedded web server. # -w=3000 # # -m|--local-networks # ntopng determines the ip addresses and netmasks for each active interface. Any traffic on # those networks is considered local. This parameter allows the user to define additional # networks and subnetworks whose traffic is also considered local in ntopng reports. All # other hosts are considered remote. If not specified the default is set to 192.168.1.0/24. # # Commas separate multiple network values. Both netmask and CIDR notation may be used, # even mixed together, for instance "131.114.21.0/24,10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0". # -m=192.168.1.0/24 # # -n|--dns-mode # Sets the DNS address resolution mode: 0 - Decode DNS responses and resolve only local # (-m) numeric IPs 1 - Decode DNS responses and resolve all numeric IPs 2 - Decode DNS # responses and don't resolve numeric IPs 3 - Don't decode DNS responses and don't resolve # -n=1 # # -S|--sticky-hosts # ntopng periodically purges idle hosts. With this option you can modify this behaviour by # telling ntopng not to purge the hosts specified by -S. This parameter requires an argu‐ # ment that can be "all" (Keep all hosts in memory), "local" (Keep only local hosts), # "remote" (Keep only remote hosts), "none" (Flush hosts when idle). # -S= # # -d|--data-dir # Specifies the data directory (it must be writable). Default directory is ./data # -d=/var/tmp/ntopng # # -q|--disable-autologout # Disable web interface logout for inactivity. # -q=
Vytvořte soubor ntopng.start:
sudo nano /etc/ntopng/ntopng.start ##Add this line## --local-networks "192.168.0.0/24" ## give your local IP Ranges here. --interface 1
Chcete-li zobrazit všechna dostupná rozhraní a možnosti, použijte ntopng -h možnost:
sudo ntopng -h
Spustit démona serveru Ntopng:
systemctl start ntopng.service systemctl start redis-server.service
Krok 4. Otestujte Ntopng.
Nyní můžete otestovat svou aplikaci Ntopng zadáním http://your-domain:3000 . Zobrazí se přihlašovací stránka Ntopng. Poprvé můžete použít uživatele „admin“ a heslo „admin“.
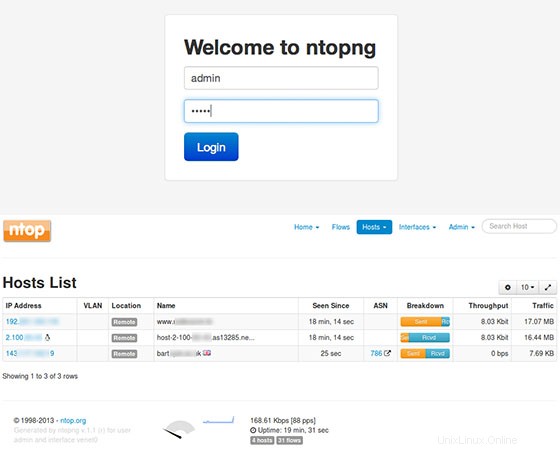
Blahopřejeme! Úspěšně jste nainstalovali Ntopng. Děkujeme, že jste použili tento návod k instalaci vysokorychlostní webové analýzy provozu Ntopng a shromažďování toků do vašeho systému Ubuntu 16.04. Další nápovědu nebo užitečné informace získáte, doporučujeme vám zkontrolovat oficiální web Ntopng.